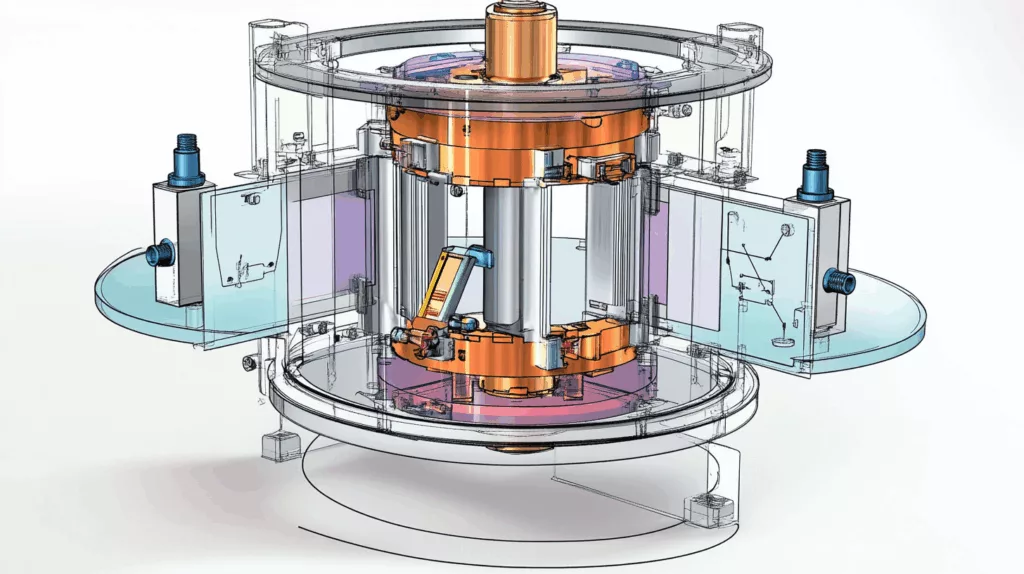
Modern industries—from robotics to aerospace—demand highly precise and responsive tools for measuring force. Among the most advanced sensing technologies available today are 3 axis force sensors, also known as triaxial force sensors. These devices can detect and measure force components simultaneously along the X, Y, and Z axes.
As XJCSENSOR is a leading manufacturer of advanced sensor technologies, understanding How 3 Axis Force Sensors Work can help engineers, technicians, and product developers implement more accurate control and feedback systems in a wide array of applications.
What Is a 3 Axis Force Sensor?
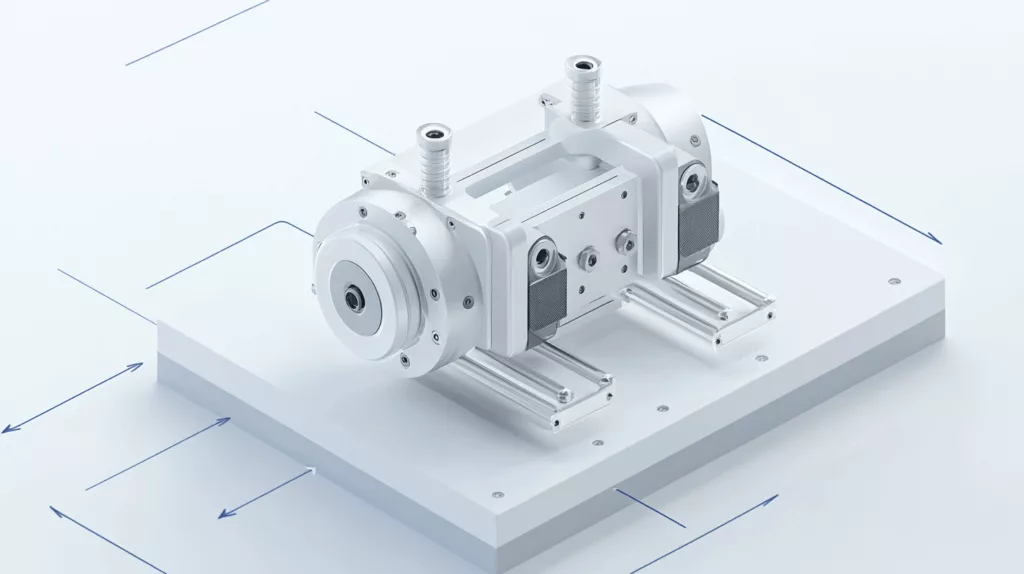
A 3 axis force sensor is a highly sensitive device engineered to measure forces in three perpendicular directions—typically referred to as the X, Y, and Z axes. This capability enables it to capture comprehensive data on how force is applied to an object or surface.
Key Features of Triaxial Force Sensors:
- Measures forces along three axes simultaneously
- High precision and stability
- Compact and durable design
- Suitable for dynamic and static force measurement
These sensors are commonly used in robotics, automation, aerospace testing, biomechanics, and industrial equipment calibration.
The Working Principle of 3 Axis Force Sensors
At the heart of a 3 axis force sensor is a multi-axis load cell, which converts applied mechanical forces into electrical signals using strain gauge technology or piezoelectric elements.
Components and Design
- Sensing Element (Load Cell): Often constructed with specialized alloys to ensure structural stability and sensitivity.
- Strain Gauges or Piezoelectric Crystals: Embedded in each axis to detect deformation or pressure.
- Signal Conditioner: Amplifies and digitizes the analog signals from each axis.
- Output Interface: Transmits data to a display or control system, typically via analog, USB, or Ethernet.
How Forces Are Measured
When force is applied to the sensor:
- The internal structure experiences strain (micro-deformation).
- Strain gauges detect the deformation on each axis.
- Each axis outputs a voltage proportional to the applied force.
- The sensor’s electronics process and combine the data into readable force vectors.
Applications of 3 Axis Force Sensors
The versatility of triaxial force sensors makes them indispensable across multiple sectors.
Robotics and Automation
- Ensures precision in robotic gripping and manipulation
- Enables force feedback in collaborative robots (cobots)
- Monitors tool wear and process forces in CNC machining
Aerospace and Defense
- Simulates and measures aerodynamic loads
- Tests materials and components under multi-directional forces
Medical and Biomechanics
- Analyzes joint movements and gait forces
- Integrates into prosthetics for real-time force monitoring
Automotive and Transportation
- Tests crash forces and component durability
- Evaluates steering and braking performance
Benefits of Using Triaxial Force Sensors
- High Sensitivity: Detects subtle variations in force application.
- Multidirectional Analysis: Offers a full vector view of how forces interact.
- Compact and Integrated: Can be embedded in small-scale systems.
- Improved Safety and Accuracy: Reduces errors in high-stakes environments.
FAQs About 3 Axis Force Sensors
Q1: Can 3 axis force sensors be customized for specific applications?
Yes, many manufacturers like XJCSENSOR offer customizable sensor solutions to fit specific dimensional, load, and environmental requirements.
Q2: Are these sensors suitable for harsh environments?
Many triaxial sensors are built with protective enclosures and rugged materials, making them ideal for industrial or outdoor use.
Q3: What’s the difference between a 3 axis sensor and a 6 axis force/torque sensor?
A 3 axis sensor measures force in three directions, while a 6 axis sensor also measures torque (rotational force) about each of those three axes.
Final Thoughts: Why Choose a 3 Axis Force Sensor?
Understanding how 3 axis force sensors work reveals why they’re a cornerstone in precision force measurement. Their ability to capture real-time, multidirectional data makes them crucial in advancing technologies that demand high responsiveness and safety.
If you’re seeking reliability and high-performance sensing, XJCSENSOR’s advanced triaxial force sensors stand out with their robust engineering and industry-grade quality. Whether you’re in R&D, manufacturing, or medical tech, integrating the right sensor can dramatically elevate your system’s performance.
Explore XJCSENSOR’s full range of 3 axis force sensors and take your application to the next level.