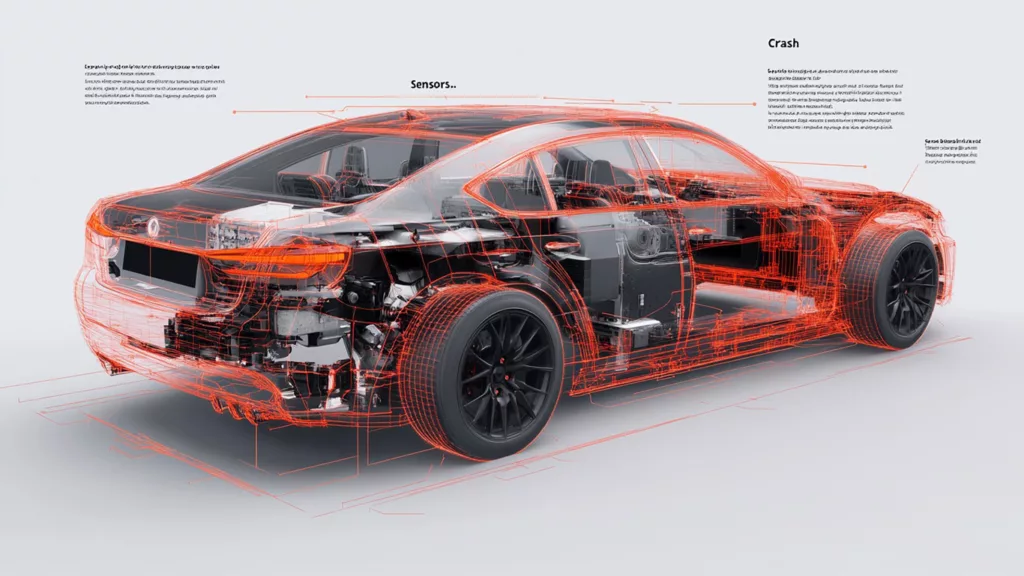
When it comes to modern automotive safety, crash sensors play a pivotal role in protecting lives. As car technology advances, understanding these sensors’ design, functionality, and importance has become crucial. This article takes a deep dive into answering the key question, How many crash sensors are in a car? while exploring the technology behind them and their essential role in preventing injuries during accidents.
Introduction
Automotive safety has undergone a seismic shift in recent decades, with crash sensors serving as unsung heroes in minimizing fatalities. From airbags to advanced autonomous systems, these sensors play a crucial role in activating life-saving measures during accidents. While many people recognize their importance, questions like How many crash sensors are in a car? often arise, shedding light on the broader topic of safety technology in vehicles.
Modern cars boast intricate networks of crash sensors that work seamlessly to ensure optimal safety. These sensors don’t just detect crashes; they predict and respond to them faster than the blink of an eye. This article unpacks the details, starting with an answer to the central question.
How Many Crash Sensors Are in a Car?
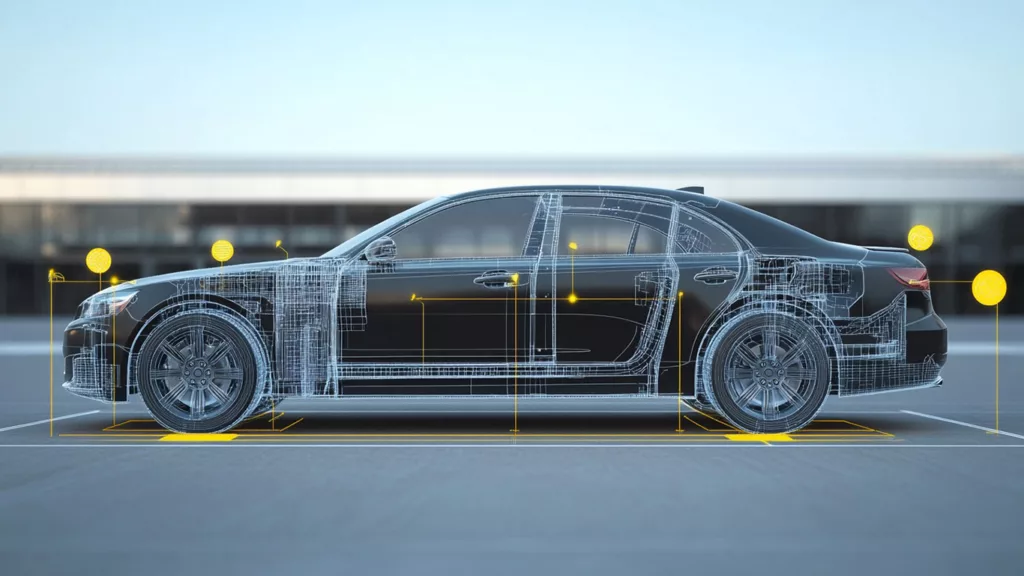
The number of crash sensors in a car varies depending on its make, model, and the level of safety features included. Typically, modern vehicles are equipped with 6 to 20 crash sensors, strategically placed throughout the car. These sensors include front-impact sensors, side-impact sensors, and rollover detection units, each contributing to comprehensive protection.
Luxury vehicles and high-end models may even feature more than 20 sensors, ensuring no stone is left unturned in terms of safety. With the rise of electric and autonomous vehicles, this number is steadily increasing, as manufacturers aim to create cars that react intelligently to even the slightest threat.
What Are Crash Sensors?
Crash sensors are small, robust devices designed to detect the sudden changes in motion, pressure, or force that occur during a collision. Once triggered, they send signals to the car’s safety systems, such as airbags and seatbelt tensioners, ensuring timely deployment. Without these sensors, modern safety systems would be far less effective.
Types of Crash Sensors
There are several types of crash sensors, each designed for a specific purpose:
- Accelerometers: Measure changes in velocity and detect impacts.
- Pressure Sensors: Monitor sudden changes in air pressure, especially useful for side impacts.
- Gyroscopes: Detect rollovers by measuring angular velocity and tilt.
- Acoustic Sensors: Listen for the sound waves of an impact or structural deformation.
Placement of Crash Sensors
Crash sensors are placed strategically across the vehicle to ensure optimal coverage. Common locations include:
- Front Bumper: For detecting frontal collisions.
- Side Doors: To respond to side-impact crashes.
- Roof and Pillars: For rollover detection.
- Rear Bumper: To address rear-end impacts.
Role of Crash Sensors in Airbag Systems
Airbags are life-saving devices, but they rely entirely on crash sensors to function. Sensors detect the severity and location of a collision, determining whether to deploy airbags. For instance, a minor fender-bender might not activate airbags, while a high-speed frontal impact will trigger them almost instantaneously.
Crash Sensors and Seatbelt Tensioners
In addition to airbags, crash sensors activate seatbelt pretensioners. These devices tighten seatbelts upon detecting an impact, ensuring passengers remain securely in place and reducing the risk of injury.
Crash Sensors in Electric Vehicles
Electric vehicles (EVs) often incorporate more advanced crash sensors compared to traditional internal combustion engine cars. Since EVs have high-voltage battery systems, sensors must also detect potential risks like thermal runaway, ensuring both crash protection and fire safety.
FAQs
How reliable are crash sensors?
Crash sensors are highly reliable due to rigorous testing and calibration by manufacturers. However, like any electronic component, they require regular maintenance.
Can crash sensors be repaired?
Crash sensors typically need replacement rather than repair, as their effectiveness relies on precision engineering.
Do all cars have the same number of crash sensors?
No, the number varies based on the car’s make, model, and safety features.
Are crash sensors expensive to replace?
Replacement costs depend on the type of sensor and the vehicle, but they are a small price to pay for safety.
What happens if a crash sensor fails?
If a sensor fails, the safety systems it controls may not activate, potentially leading to increased risk during an accident.
Do crash sensors work in all weather conditions?
Yes, crash sensors are designed to function effectively in various weather conditions, from extreme heat to freezing cold.
Conclusion
Crash sensors are integral to modern automotive safety, offering swift, reliable responses to collisions. From the question How many crash sensors are in a car? to their role in advanced safety systems, understanding these components underscores their life-saving potential. As technology continues to evolve, crash sensors will undoubtedly become even more sophisticated, safeguarding passengers in ways we can only imagine today.