Introduction
Pressure measurement is essential in various industries, from industrial automation to healthcare and automotive applications. Understanding how to measure pressure accurately can optimize system performance, enhance safety, and improve efficiency. In this guide, we will explore the different types of pressure measurement techniques, sensor applications, and best practices for obtaining precise readings.
Understanding Pressure Measurement
Pressure is defined as the force exerted per unit area and is commonly measured in Pascals (Pa), bar, or psi (pounds per square inch). Depending on the application, different types of pressure measurements are used:
- Absolute Pressure: Measured relative to a perfect vacuum.
- Gauge Pressure: Measured relative to atmospheric pressure.
- Differential Pressure: Measures the difference between two pressure points.
Types of Pressure Sensors
To measure pressure accurately, various sensors are available, each suitable for different applications:
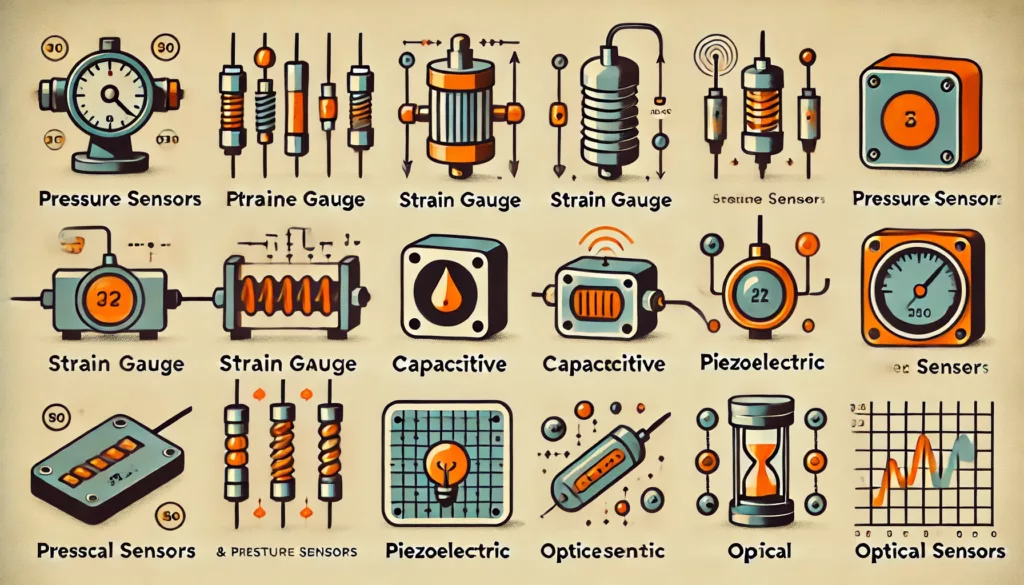
1. Strain Gauge Pressure Sensors
Strain gauge sensors convert pressure into electrical resistance changes, providing accurate measurements. They are widely used in industrial automation and aerospace applications.
2. Capacitive Pressure Sensors
These sensors detect changes in capacitance caused by pressure variations. They are commonly found in medical devices and consumer electronics.
3. Piezoelectric Pressure Sensors
Piezoelectric sensors generate an electrical charge in response to pressure changes. They are ideal for dynamic pressure measurements in automotive and industrial settings.
4. Optical Pressure Sensors
Using fiber optics, these sensors measure pressure changes based on light intensity variations. They are highly resistant to electromagnetic interference, making them suitable for harsh environments.
Applications of Pressure Measurement Sensors
1. Industrial Automation
Pressure sensors are integral to monitoring hydraulic and pneumatic systems, ensuring optimal operation and safety in manufacturing and process industries.
2. Automotive Industry
Vehicles rely on pressure sensors for tire pressure monitoring systems (TPMS), engine performance optimization, and fuel injection control.
3. Medical Equipment
Devices such as blood pressure monitors and ventilators depend on accurate pressure sensors for reliable patient care and diagnostics.
4. Environmental Monitoring
Barometric pressure sensors help meteorologists predict weather conditions, while water pressure sensors play a role in hydrology studies.
Best Practices for Accurate Pressure Measurement
To ensure precise pressure readings, follow these best practices:
- Choose the Right Sensor: Select a sensor based on the pressure range, environmental conditions, and application requirements.
- Calibrate Regularly: Periodic calibration ensures accuracy and prevents measurement drift.
- Consider Temperature Effects: Temperature variations can impact sensor performance; compensate for these changes where necessary.
- Maintain Proper Installation: Avoid mounting errors, leaks, or contamination that can affect sensor readings.
Conclusion
Knowing how to measure pressure accurately is critical for various applications across multiple industries. By selecting the right sensor and following best practices, you can achieve precise pressure measurements, improve efficiency, and enhance system reliability. Whether in industrial automation, automotive, healthcare, or environmental monitoring, pressure sensors play a crucial role in optimizing performance and safety.