Introduction
As robotics continues to evolve, the integration of joint sensor technology has become a game-changer in automation, artificial intelligence, and industrial applications. These sensors allow robots to move with precision, detect environmental changes, and interact seamlessly with humans and objects.
From manufacturing lines to medical robotics, joint sensor technology is revolutionizing how machines operate, making them more efficient, responsive, and intelligent. In this article, we’ll explore the working principles, types, applications, and future advancements of joint sensors in robotics.
What is a Joint Sensor in Robotics?
A joint sensor in robotics is a device used to measure and monitor the movement, position, and torque of robotic joints. These sensors play a crucial role in enabling robots to perform complex motions with high accuracy.
By gathering real-time data on joint angles, force, and speed, these sensors ensure smooth operation in robotic arms, exoskeletons, humanoid robots, and industrial automation systems.
How Does a Joint Sensor Work in Robots?
Joint sensors function by detecting physical changes in robotic joints and converting them into digital signals for analysis. Depending on the type of sensor, they measure:
- Angular Displacement– Determines the rotation angle of a joint.
- Torque and Force– Measures the load applied on the joint.
- Speed and Acceleration– Tracks movement dynamics.
- Environmental Feedback– Provides sensory data for adaptive responses.
Once collected, this data is processed through control algorithms that adjust robotic movements for greater precision and efficiency.
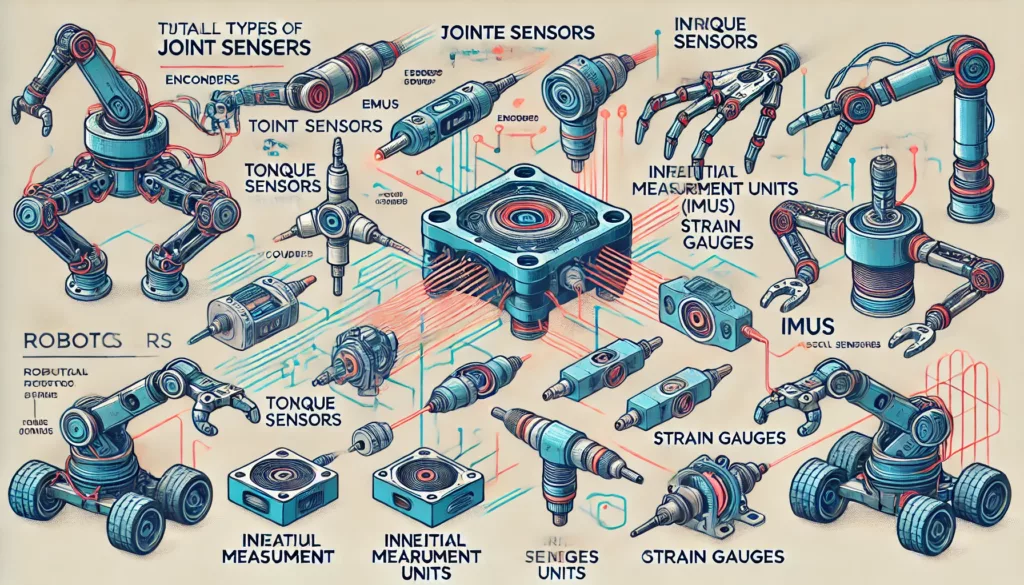
Types of Joint Sensors Used in Robotics
Encoders
Encoders measure the position and velocity of robotic joints, ensuring accurate motion control. They are widely used in industrial automation and robotic arms.
Strain Gauges
These sensors detect mechanical stress and deformation in robotic joints, helping in force control applications such as gripping and lifting objects.
Torque Sensors
Torque sensors measure the force applied to robotic joints, crucial for collaborative robots (cobots) that require safe human interaction.
Inertial Measurement Units (IMUs)
IMUs combine accelerometers and gyroscopes to track motion, orientation, and acceleration of robotic limbs.
Hall Effect Sensors
These sensors use magnetic fields to measure rotational movement, providing non-contact position sensing for robotic applications.
Optical Sensors
Using infrared or laser technology, optical sensors enable high-precision motion tracking in robotic systems.
Applications of Joint Sensors in Robotics
1. Industrial Automation
Joint sensors ensure precise robotic arm movements in assembly lines, welding, and packaging, improving efficiency and reducing human error.
2. Collaborative Robots (Cobots)
Cobots work alongside humans in factories, using joint sensors to detect human presence and adjust force levels for safe interactions.
3. Medical Robotics
Surgical robots utilize joint sensors to perform minimally invasive procedures with unparalleled accuracy and control.
4. Humanoid Robots
These robots rely on joint sensors to mimic human-like movements, enabling them to walk, grasp objects, and interact with their environment.
5. Exoskeletons and Wearable Robotics
Joint sensors assist in rehabilitation by providing feedback for movement correction, helping individuals regain mobility.
6. Autonomous Vehicles and Drones
Robots in autonomous systems use joint sensors to stabilize movements, adapt to terrain changes, and enhance navigation.
Advantages of Joint Sensors in Robotics
- Enhanced Precision– Enables robots to perform delicate and complex tasks.
- Real-time Motion Control– Adjusts movements instantly for better accuracy.
- Safety Improvements– Helps prevent collisions in human-robot interactions.
- Energy Efficiency– Optimizes movement, reducing unnecessary power consumption.
- Increased Automation– Reduces manual intervention, improving productivity.
Challenges and Limitations of Joint Sensors in Robotics
Despite their advantages, joint sensors in robotics also face some challenges:
- Sensor Drift– Over time, some sensors may experience slight inaccuracies in measurements.
- Cost of High-Precision Sensors– Advanced joint sensors can be expensive.
- Complex Integration– Requires sophisticated algorithms for seamless operation.
- Environmental Factors– Temperature and electromagnetic interference may affect sensor performance.
Future Innovations in Robotic Joint Sensors
As robotics advances, so does the technology behind joint sensor systems. Key trends shaping the future include:
- AI-Powered Motion Prediction– Machine learning algorithms will improve sensor accuracy and response time.
- Miniaturization and Wearable Robotics– Smaller, lightweight sensors will enhance the usability of exoskeletons and medical robots.
- Wireless Joint Sensors– 5G and IoT integration will enable real-time data transmission for remote robot control.
- Self-Calibrating Sensors– Advanced sensors will adjust automatically to reduce drift and errors.
These developments will further enhance robotic capabilities, making them more autonomous and intelligent.
FAQs
What is a joint sensor in robotics?
Why are joint sensors important in industrial robots?
How do torque sensors improve collaborative robots?
Can joint sensors be used in medical robotics?
What are the main types of joint sensors?
What is the future of joint sensors in robotics?
Conclusion
The integration of joint sensor technology in robotics is transforming industries by enhancing precision, automation, and human-robot collaboration. Whether in industrial automation, medical robotics, or humanoid applications, these sensors provide the foundation for smarter, safer, and more efficient machines.
As sensor technology continues to advance, robots will become even more capable, adaptable, and intelligent, paving the way for a future where automation seamlessly integrates into everyday life.
Call-to-Action (CTA)
Are you looking to integrate joint sensor technology into your robotic applications? Contact XJCSENSOR for innovative solutions in wearable technology and smart automation. Let’s build the future of robotics together! 🚀